Choosing the Right Genome Reference for Human Gut Microbiota Analysis

When analysing the human gut microbiota through DNA sequencing, selecting an appropriate reference genome database is crucial. These references allow researchers to map sequencing reads accurately to known genomes. Here is what you need to know when choosing a reference genome database for gut microbiota.
Why Genome References Are Essential for Unlocking the Gut Microbiome
Without comprehensive and precise reference collections, there is a significant risk of failing to map many sequences, which could obscure key insights into the microbiome. A ground-breaking resource in this field is the HumGut database, which offers a high-quality collection of prokaryotic genomes specifically tailored for human gut microbiota research. This collection features genomes that are highly relevant to populations from around the globe, making it an invaluable tool in microbiome studies.
UHGG: A Landmark in Gut Microbiota Genomic Resources
In 2021, the UHGG catalogue was introduced, which marked a major advance in gut microbiome research. It contains over 200,000 genomes representing 4,644 species, a vast and unprecedented repository. Importantly, many of these genomes were constructed using metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs), which allow researchers to infer the presence of species that have not yet been cultured in the lab. These MAGs offer critical insights into the diversity of species residing in the human gut based purely on their genetic material, opening the door to studying microbial species that remain poorly understood.
HumGut: A Globally Relevant Database for Microbiome Studies
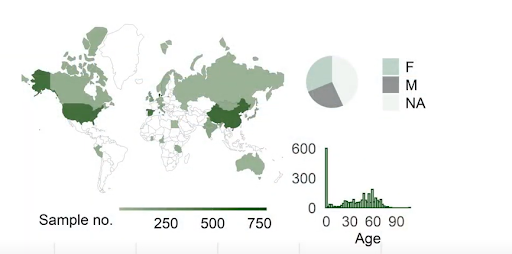
While UHGG provided a massive repository of gut microbiota genomes, there remained the question of global relevance—do these genomes accurately represent healthy individuals from various regions worldwide? HumGut, which also debuted in 2021, addresses this gap. By analysing over 3,500 metagenomes collected from healthy individuals across diverse geographic locations—including Denmark, the U.S., China, Tanzania, and Peru—HumGut assembles a database of approximately 30,000 genome representatives. Each genome in this collection is clustered with at least 97.5% similarity to others in its group, ensuring a high level of accuracy. This precision is vital for developing targeted diagnostics and therapeutic strategies for gut microbiota-related conditions.
HumGut: Fewer Gaps, More Insights in Gut Microbiome Analysis
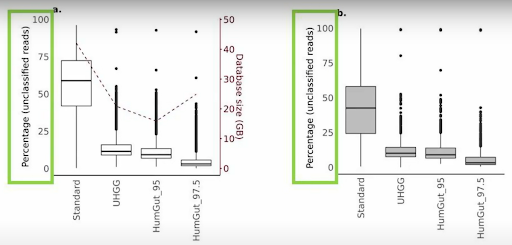
One of the key advantages of HumGut is that it exclusively includes genomes that have been identified in actual human gut samples, providing unparalleled relevance to researchers. If a genome is present in HumGut, it has been found in at least one real-world sample. HumGut outperforms existing reference databases by offering significantly fewer unclassified reads when analyzing metagenomic data from human gut samples. This capability is essential in ensuring that researchers can identify more sequences accurately, reducing the risk of missing critical microbial species.
Tailored for the Gut: Why HumGut Is a Step Ahead of UHGG
Although HumGut and UHGG share similarities—HumGut incorporates genomes from UHGG and the NCBI RefSeq prokaryote genomes—the main difference lies in their refinement. HumGut’s genomes were (bioinformatically) filtered and selected based on their presence in human gut metagenomes. This ensures a higher level of biomedical relevance, as only genomes with demonstrated biological significance are included. This tailored approach makes HumGut a superior choice for researchers focused on the human gut microbiome, as it provides a more relevant and customized genome collection.
From Downloads to Discoveries: Leveraging HumGut for High-Resolution Gut Analysis
A high-quality reference genome collection like HumGut is essential for conducting high-resolution metagenomic analyses. Researchers can download FASTA files from HumGut to build custom databases for taxonomic profiling tools such as Kraken2. The public availability of HumGut makes it accessible for widespread use, and while it is still in the early stages of adoption, more research groups are beginning to incorporate it into their workflows, further solidifying its value in the field.
Advancing Diagnostics and Therapy with Comprehensive Microbiome Databases
The advent of comprehensive databases like HumGut and UHGG has revolutionized human gut microbiota research. By offering highly relevant, biologically validated genome collections, these databases empower scientists to deepen our understanding of the gut microbiome’s complexity. In particular, HumGut’s emphasis on high-quality, globally relevant genomes sets it apart as a superior reference tool, paving the way for novel diagnostic and therapeutic advancements. As researchers continue to explore the intricacies of the gut microbiota, the use of resources like HumGut will prove instrumental in unlocking the full potential of microbiome science.
